java入门学习过程
相遇皆是缘分
初次体验
HelloWorld
1 | public class HelloWorld{ |
基础语法
注释
1 | 单选注释 // |
关键字
关键字的字母全部小写
代码编辑器中关键字有颜色标记
1 | public class static 等等都是关键字 |
字面量
数据在程序中的书写格式
| 字面量类型 | 说明 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 整数类型 | 不带小数点的数字 | 666 , -88 |
| 小数类型 | 带小数点的数字 | 13.14 , -5.21 |
| 字符串类型 | 用双引号括起来的内容 | “HelloWorld” , “黑马程序员” |
| 字符类型 | 用单引号括起来的,内容只能有一个 | ‘A’ , ‘0’ , ‘我’ |
| 布尔类型 | 布尔值,表示真假 | 只有两个值 : true , false |
| 空类型 | 一个特殊的值,空值 | 值是: null |
1 | public class HelloWorld{ |
扩展点:特殊字符 ‘\t’ ‘\r’ ‘\n’ …
变量
数据类型 变量名 = 数据值;
1 | public class HelloWorld{ |
数据类型
数据类型分成:基本数据类型、引用数据类型
注意取值范围
整数和小数取值范围大小关系: double > float > long > int > short > byte
1 | public class HelloWorld{ |
小练习
1 | public class HelloWorld{ |
标识符
就是给 类、方法、变量 等起的名字
1 | 硬性要求: |
键盘录入
Scanner 类:就可以接收键盘输入的数字
1 | 1.导包 |
获取随机数
1 | //导包 |
小练习
1 | // 1.导包 |
运算符
算术运算符
1 | package day3; |
小练习-数值拆分
键盘录入一个三位数,将其拆分为个位,十位,百位后,打印在控制台
1 | package day3; |
数字相加
取值范围: byte < short < int < long < float < double
| 隐式转换 | 强制转换 |
|---|---|
| 取值范围小的数值——> 取值范围大的数值 | 取值范围大的数值——> 取值范围小的数值 |
| byte 、short 、char 在数据运算的时候,会提升为 int 再进行运算 | 格式: 目标数据类型 变量名 = (目标数据类型)被强转的数据; double a = 12.3; int b = (int)a; |
小练习
1 | 问题:请问最终的运算结果是什么类型的? |
字符串相加
当 “+” 操作中出现字符串时,这个 “+” 是字符串连接符,而不是算术运算符了
1 | "123" + 123 // "123456" |
小练习
1 | //看代码说结果 |
字符相加
当 “+” 操作中出现字符时,字符将转成ASCLL码值,进行计算
1 | char c='a'; |
小练习
1 | //看代码说结果 |
自增自减运算符
| 符号 | 作用 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ++ | 加 | 变量的值加1 |
| – | 减 | 变量的值减1 |
++ 和 – 既可以放在变量的前边,也可以放在变量的后边
i++ 先用后加 ++i 先加后用
1 | int a = 10; |
赋值运算符
+= 、 -= 、*= 、 /= 、%= 底层隐藏了一个强制类型转换
1 | // += |
关系运算符
逻辑运算符
&(逻辑与) |(逻辑或) 无论左边是真是假,右边都会判断真假,两边都需要判断,效率偏低
短路逻辑运算符
&&(短路与) 当左边为真时,才会判断右边是否为真; 当左边为假时,不再判断右边是否为真假,整体直接为 假
||(短路或) 当左边为真时,不再判断右边是否为真假,整体直接为 真 ; 当左边为假时,才会判断右边是否为假
效率高
小练习
1 | package day3; |
三元运算符
格式: 关系表达式?表达式1:表达式2;
1 | 求两个数的最大值 |
运算符优先级
其他运算符
用于二进制 原码、反码、补码
判断和循环
顺序结构
if
1 | 格式: |
分支结构
switch
1 | switch(表达式){ |
小练习
1 | package day4; |
循环结构
for
1 | for(初始化语句;条件判断语句;条件控制语句){ |
while
1 | 初始化语名; |
do…while 循环
1 | 初始化语名; |
循环高级
无限循环
1 | for(;;){ |
跳转控制语句
1 | contioue; 跳过本次循环,执行下次循环 |
数组
数据格式
1 | 格式一: |
数组元素访问
1 | 格式: |
数组的遍历
1 | int[] arr={11,22,33,44}; |
数组的动态初始化
1 | 格式: |
方法
方法是程序中最小的执行单元
重复的代码、具有独立功能的代码打一个包,需要用时调用包即可
类似于c语言的函数调用
方法定义
1 | 格式: |
带参数定义
1 | 格式: |
带返回值方法的定义和调用
1 | 格式: |
方法的重载
1 | 同一个类中,方法名相同,参数不同的方法 |
小练习
1 | //数据中找出最大值 |
方法的值传递
1 | //形参的改变,不影响实际参数的值 |
前面的综合练习
卖飞机票
1 | package day4; |
找质数
1 | package day4; |
验证码
1 | package day4; |
1 | package day4; |
数字加密
1 | package day4; |
抢红包
1 | package day4; |
双色球系统
1 | package day4; |
面向对象
面向:拿、找
对象:能干活的东西
面向对象编程:拿东西过来做对应的事情
1 | 学习获取已有对象并使用(比如,用到了随机数) |
类和对象
如何定义类
1 | public class 类名{ // 类名要与文件名一致 |
如何得到类的对象
1 | 类名 对象名 = new 类名(); |
如何使用对象
1 | 访问属性:对象名.成员变量 |
day4
1 | package day4; |
Phone
1 | package day4; |
封装
原则:对象代表什么,就得封装对应的数据, 并提供数据对应的行为
1 | // 对象代表什么,就得封装对应的数据, 并提供数据对应的行为 |
1 | 需要 : 人关门,请针对这个需要进行面向对象设计 |
私有关键字 — private
会更安全
GirlFriend
1 | package day4; |
day4
1 | package day4; |
this 关键字
成员变量和局部变量
1 |
|
构造方法
1 | // 作用:在创建对象的时候给成员变量进行初始化的。 |
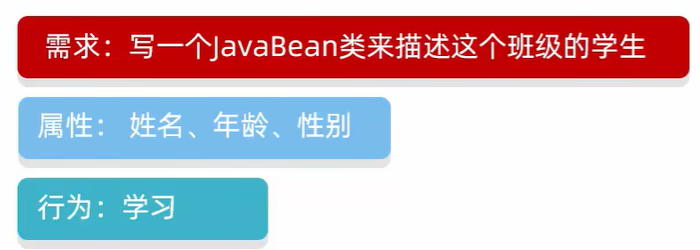
标准的 javabean 类
快捷键一键生成标准的 javabean 类
基本数据类型和引用数据类型
1 | 基本数据类型 引用数据类型 |
面向对象综合练习
文字版格斗游戏
第一版
day4.java
1 | package day4; |
role.java
1 | package day4; |
第二版
day4.java
1 | package day4; |
role.java
1 | package day4; |
对象数组
1
day5.java
1 | package day5; |
Goods.java
1 | package day5; |
2
day5.java
1 | package day5; |
Goods.java
1 | package day5; |
3
day5.java
1 | package day5; |
phone.java
1 | package day5; |
4
day5.java
1 | package day5; |
GirlFriend.java
1 | package day5; |
5
day5
1 | package day5; |
student.java
1 | package day5; |
字符串
API
1 | API: |
使用步骤:
显示—索引—输入你要查找的关键字—显示
String
字符串的比较
== 号比较的是什么?
| 基本数据类型(int) | 引用数据类型(String) |
|---|---|
| 基本数据类型比较的是数据值 | 引用数据类型比较的是地址值 |
1 | package index; |
字符串内容比较
| equals 方法 | equalsIgnoreCase方法 |
|---|---|
| 完全一样结果才是 true ,否则为 false | 忽略大小写的比较 |
1 | package index; |
综合练习
用户登录
1 | package index; |
遍历字符串
| 字符串对象.charAt(int index) | 字符串对象.length() |
|---|---|
| 遍历字符串 | 字符串的长度 |
1 |
|
统计字符次数
1 | package index; |
拼接字符串
1 | package index; |
字符串反转
1 | package index; |
金额转换
1 | package index; |
手机号屏蔽
| 字符串.substring(int a,int b) | 字符串.substring(int a) |
|---|---|
| 从a截取到b,包括a,包括b | 从a截取到尾未 |
1 | package index; |
身份证信息查看
1 | package index; |
敏感词替换
| 字符串.replace(旧值,新值) | |
|---|---|
| 替换 只有返回值才是替换之后的结果 |
1 | package index; |
StringBuijlder
操作效率更高
综合练习
创建方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public StringBuilder() | 创建一个空白可变字符串对象,不含有任何内容 |
| public StringBuilder(String str) | 根据字符串的内容,来创建可变字符串对象 |
常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public StringBuilder append(任意类型) | 添加数据,并返回对象本身 |
| public StringBuilder reverse() | 反转容器中的内容 |
| public int length() | 返回长度(字符出现的个数) |
| public String toString() | 通过toString()就可以实现把 String Builder 转换为 String |
1 | package index; |
对称字符串
1 | package index; |
拼接字符串
1 | package index; |
StringJoiner
提高字符串的操作效率,代码也简洁
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public StringJoiner(间隔符号) | 创建一个StringJoiner对象,指定拼接时的间隔符号 |
| public StingJoiner(间隔符号,开始符号,结束符号) | 创建一个StringJoiner对象,指定拼接时的间隔符号、开始符号、结束符号 |
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public StringJoiner add(添加的内容) | 添加数据,并返回对象本身 |
| public int length() | 返回长度(字符出现的个数) |
| public String toString() | 返回一个字符串(该字符串就是拼接之后的结果) |
1 | package index; |
综合大练习
转换罗马数字
1 | package index; |
调整字符串
1 | package index; |
1 | package index; |
集合 – ArrayList
1 | 集合与数组的区别: |
集合的基本使用
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 增 boolean add(Ee) | 添加元素,返回值表示是否添加成功 |
| 删 boolean remove(Ee) | 删除指定元素,返回值表示是否删除成功 |
| 删 E remove(int index,E e) | 删除指定索引的元素,返回被删除元素 |
| 改 E set(int index,E e) | 修改指定索引的元素,返回原来的元素 |
| 查 E get(int index) | 获取指定索引的元素 |
| int size() | 集合的长度,也就是集合中元素的个数 |
1 | package index; |
练习
字符串集合的遍历
1 | package index; |
基本数据类型对应的包装类
Int类型集合的遍历
index.java
1 | package index; |
Student.java
1 | package index; |
添加学生对象并遍历
1 | package index; |
index.java
1 | package index; |
Student.java
1 | package index; |
添加用户对象并判断是否存在
index.java
1 | package day6; |
user.java
1 | package day6; |
添加手机对象并返回要求的数据
day6.java
1 | package day6; |
phone.java
1 | package day6; |
学生管理系统
day7.java
1 | package day7; |
student.java
1 | package day7; |
面向对象进阶
static
| 被static修饰的成员变量,叫做静态变量 | 被static修饰的成员方法,叫做静态方法 |
|---|---|
| 特点:被该类所有对象共享 | 特点:多用在 测试类 和 工具类 中 |
| 调用方式:1.类名调用 2.对象名调用 | 调用方式:1.类名调用 2.对象名调用 |
Student.java
1 | package day9; |
index.java
1 | package day9; |
工具类
帮助我们做一些事情的,但是不描述任何事物的类
| Javabean类 | 测试类 | 工具类 |
|---|---|---|
| 用来描述一类事物的类。比如:Student,Teacher,Dog,Cat等 | 用来检查其他类是否书写正确,带有main方法的类,是程序的入口 | 不是用来描述一类事物的,而是帮我们做一些事情的类 |
| 工具类 | |
|---|---|
| 1、类名见名知意 | |
| 2、私有化构造方法 | public class Student { private Student(){} } |
| 3、方法定义为静态 | public class Student { private Student(){ public static int getMax { } } } |
定义数组工具类
ArrayUtil.java
1 | package day9; |
index.java
1 | package day9; |
定义学生工具类
StudentUtil.java
1 | package day9; |
Student.java
1 | package day9; |
index.java
1 | package day9; |
static的注意事项
静态方法中,只能访问静态
非静态方法可以访问所有
静态方法中没有this关键字
继承
1 | public class Student extends Person{} |
多层继承
构造方法
构造方法 非私有 不能继承父类 private 不能继承父类
成员变量
成员变量 非私有 能继承父类 private 能(但不能直接使用)
方法成员
成员方法 非私有 能继承父类 private 不能继承父类
继承中:成员变量的访问特点
继承中:成员方法的访问特点
!
练习:利用方法的重写设计继承结构
1 | package day9; |
继承中:构造方法的特点
多态
Text.java 父类
1 | package day11; |
Person.java 父类
1 | package day11; |
Student.java 子类
1 | package day11; |
Teacher.java 子类
1 | package day11; |
Adminstrator.java 子类
1 | package day11; |
多态的优势和弊端
instanceof
多态综合练习
index.java
1 | package day12; |
Animal.java
1 | package day12; |
car.java
1 | package day12; |
dog.java
1 | package day12; |
Person.java
1 | package day12; |
包、final、权限修饰符、代码块
抽象类
1.抽象类不能实例化(抽象类不能创建对象)
2.抽象类中不一定有抽象方法,有抽象方法的类一定是抽象类
3.可以有构造方法
4.抽象类的子类
抽象类为父类时
子类要么是也是抽象类 (但会无法创建对象) 不常用
要么重写父类中的所有抽象方法(可以创建对象)常用
综合练习
index.java
1 | package day13; |
Animal.java
1 | package day13; |
Dog.java
1 | package day13; |
frog.java
1 | package day13; |
Sheep.java
1 | package day13; |
接口
接口的定义和使用
接口常运用于子类,抽象常运用于父类
接口就是一种规则,是对行为的抽象
接口练习使用
Test.java
1 | package day14; |
Animal.java
1 | package day14; |
Swim.java(接口)
1 | package day14; |
Frog.java
1 | package day14; |
Dog.java
1 | package day14; |
Rabbit.java
1 | package day14; |
接口的细节:成员特点和接口的各种关系
综合练习
分析
Test.java
1 | package day15; |
Proson.java
1 | package day15; |
Sporter.java
1 | package day15; |
Coach.java
1 | package day15; |
English.java
1 | package day15; |
PingPangSporter.java
1 | package day15; |
PingPangCoach.java
1 | package day15; |
BasketBallCoach.java
1 | package day15; |
BasketBallSporter.java
1 | package day15; |
内部类
类的五大成员:
属性、方法、构造方法、代码块、内部类
基本使用
成员内部类(了解)
写在成员位置的,属于外部类的成员
1 | public class Car { //外部类 |
静态内部类(了解)
局部内部类(了解)
匿名内部类(掌握)
1 | 格式: |
运用场景
常用API
快速过一遍,多用用 JDK-API 查一查
Math
用法 :Math.方法名()
System
System.方法名()
计算机中的时间原点 1970年1月1日 00:00:00 我们国家 1970年1月1日 08:00:00
1 | package day18; |
1 | package day18; |
1 | package day18; |
Runtime
Runtime.方法名()
1 | package day18; |
Object
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String toString() | 返回对象的字符串表示形式 |
| public boolean equals(Object obj) | 比较两个对象是否相等 |
| protected Object clone(int a) | 对象克隆 |
1 | package day19; |